Sails
From CruisersWiki
Contents |
Sails
Introduction to Yacht's Sails
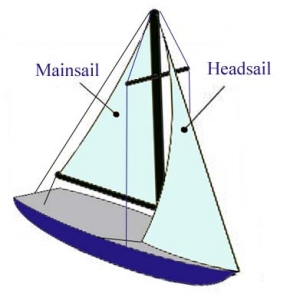
The most common sail plan for cruising yachts is the Sloop. This has two sails in a fore-and-aft arrangement: the mainsail and the jib.
The mainsail extends aftward and is secured the whole length of its edges to the mast and to a boom also hung from the mast.
The jib is secured along its leading edge to a forestay strung from the top of the mast to the bowsprit on the bow of the boat. A genoa is also used on many cruising yachts - it is a type of jib that is large enough to overlap the mainsail, and cut so that it is fuller than an ordinary jib.
Fore-and-aft sails can be switched from one side of the boat to the other in order to provide propulsion as the sailboat changes direction relative to the wind. When the boat's stern crosses the wind it is called gybing and when the bow crosses the wind, it is called tacking. Tacking repeatedly from port to starboard and/or vice versa, called "beating", is done in order to allow the boat to follow a course into the the wind.
A primary feature of a properly designed sail is an amount of draft, caused by the curvature of the surface of the sail. When the leading edge of a sail is oriented into the wind, the correct curvature helps maximise lift while minimising turbulence and drag, much like the carefully designed curves of aircraft wings. Modern sails are manufactured with a combination of broadseaming and non-stretch fabric. The former adds draft, while the latter allows the sail to keep a constant shape as the wind pressure increases. The draft of the sail can be reduced in stronger winds by use of a cunningham and outhaul, and also by bending the mast and increasing the downward pressure of the boom by use of a boom vang.
Aerodynamics of Sails
Sails propel the boat in one of two ways. When the boat is going in the direction of the wind (i.e. downwind), the sails may be set merely to trap the air as it flows by. Sails acting in this way are aerodynamically stalled. In stronger winds, turbulence created behind stalled sails can lead to aerodynamic instability, which in turn can manifest as increased downwind rolling of the boat. Spinnakers and square-rigged sails are often trimmed so that their upper edges become leading edges and they operate as airfoils again, but with airflow directed more or less vertically downwards. This mode of trim also provides the boat with some actual lift and may reduce both wetted area and the risk of "digging in" to waves.
The other way sails propel the boat occurs when the boat is traveling across or into the wind. In these situations, the sails propel the boat by redirecting the wind coming in from the side towards the rear. In accordance with the law of conservation of momentum, air is redirected backwards, making the boat go forward. This driving force is called lift although it acts largely horizontally.
On a sailing boat, a keel or centreboard helps to prevent the boat from moving sideways. The shape of the keel has a much smaller cross section in the fore and aft axis and a much larger cross section on the athwart axis (across the beam of the boat). The resistance to motion along the smallest cross section is low while resistance to motion across the large cross section is high, so the boat moves forward rather than sideways. In other words it is easier for the sail to push the boat forward rather than sideways. However, there is always a small amount of sideways motion, or "leeway".
Forces across the boat are resolved by balancing the sideways force from the sail with the sideways resistance of the keel or centerboard. Also, if the boat heels, there are restoring forces due to the shape of the hull and the mass of the ballast in the keel being raised against gravity. Forward forces are balanced by velocity through the water and friction between the hull, keel and the water.
Measurement
Details?
Fitting
Details?
Maintenance
Details?
.