North Sea
From CruisersWiki
| North Sea
| |
| |
The North Sea is a marginal, epeiric sea of the Atlantic Ocean on the European continental shelf. It is more than 600 miles (970 km) long and 350 miles (560 km) wide, with an area of around 222,000 square miles (570,000 km2). A large part of the European drainage basin empties into the North Sea including water from the Baltic Sea. The North Sea connects with the rest of the Atlantic through the Dover Strait and the English Channel in the south and through the Norwegian Sea in the north.
The North Sea averages about 100 m (325 ft) deep, with a maximum depth of 700 m (2300 ft) and in some areas shallows can be a mere 15 m deep.
For the most part, the sea lies on the European continental shelf. The only exception is the Norwegian trench, a narrow area of the northern North Sea off Norway. The North Sea is bounded by Great Britain to the west and the northern and central European mainland to the east and south, including Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France.
In the south-west, the North Sea becomes the English Channel beyond the Straits of Dover. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat. In the north, it opens in a widening funnel shape to the Norwegian Sea, which lies in the very north-eastern part of the Atlantic.
Apart from the obvious boundaries formed by the coasts of the countries which border it, the North Sea is generally considered to be bounded by an imaginary line from Lindesnes, Norway to Hanstholm, Denmark running towards the Skagerrak. However, for statistical purposes, the Skagerrak and the Kattegat are sometimes included as part of the North Sea. The northern limit is less well-defined. Traditionally, an imaginary line is taken to run from northern Scotland, by way of Shetland, to Ålesund in Norway. According to the Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the North-East Atlantic of 1962 it runs further to the west and north from longitude 5° West and latitude 62° North, at the latitude of Geirangerfjord in Norway.
Charts
- Source
- Chart Number - Chart Name
- Chart Number - Chart Name
- Source
- Chart Number - Chart Name
Weather
Give weather conditions in the region or refer to another page (a country?) that covers these conditions.
Sources for weather information
- Shipping Forecast, isued by the Met. Office and promulgated by the B.B.C.
- Atlantic Surface Pressure Chart from the B.B.C. - a very useful feature.
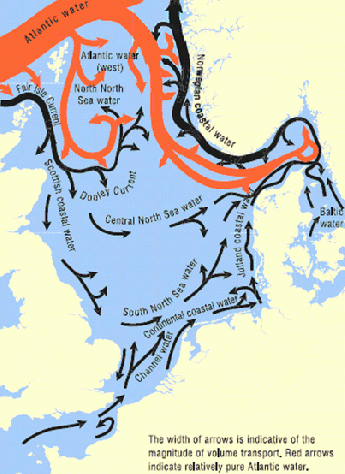
Currents & Tides
The tides are caused by the tide wave from the North Atlantic, as the North Sea itself is too small and too flat to have its own tides. Ebb and flow alternate in a cycle of 12.5 hours. The tide wave, owing to the Coriolis effect, flows around Scotland and then counter-clockwise along the English coast, reaching the German Bight some 12 hours after arriving in Scotland. In so doing, it runs around three amphidromic points: a central point lies shortly before the Straits of Dover. It is formed by the tide wave which is transported through the English Channel. It influences the tides in the narrow area in the Southern Bight between southern [England]] and the Netherlands. The other amphidromic system consists of two points close to each other, which form a tide wave. The two other points just off the coast of southern Norway and lying on a line between southern Denmark and the West Frisian Islands form one single area around which the tides flow. Its central point lies off the coast of Denmark at 55° 25' N, 5° 15' E.
As a result, the tidal range in southern Norway is less than half a metre (1.5 ft), but increases the further any given coast lies from the amphidromic point. Shallow coasts and the funnel effect of narrow straits increase the tidal range. The tidal range is at its greatest at The Wash on the English coast, where it reaches 6.80 m (22 ft). In shallow water areas, the real tidal range is strongly influenced by other factors, such as the position of the coast and the wind at any given moment or the action of storms. In river estuaries, high water levels can considerably amplify the effect of high tide.
Passages
List popular passages/routes, timing, etc.
Communication
Add here VHF channel for coastguard, harbor masters. etc.
Also see World Cruiser's Nets.
Any navigation notes here. If this section does not apply remove it.
Health & Security
Submit any health warnings/information and any security details here. If this section does not apply remove it.
Countries
Forums
List links to discussion threads on partnering forums. (see link for requirements)
Links
- North Sea at the Wikipedia
- North Sea at the Wikivoyage
- British Admiralty Charts & Publications, on-line catalogue
Links
List links external to the wiki such as in Wikipedia & Wikivoyage.
For Wikipedia you can use the Wikipedia template & for the Wikivoyage the Wikivoyage template.
References
Books, Guides, etc. Use the Reference template or not at your discretion. For example:
-
{{Reference|Rod Heikel|Greek Waters Pilot Imray||Laurie and Wilson, Cambridgeshire|9780852889718}}, expands to - Rod Heikell, Greek Waters Pilot Imray, Laurie and Wilson, Cambridgeshire, ISBN 9780852889718
- Author, Title, Publisher, ISBN ISBN number
- Author, Title, Publisher, ISBN ISBN number
You may want to remove the above entries and use instead a link to the Country or Region that lists the relevant references. If so enter, after removing {{MagentaText|xx}}, the following:
See [[Country or Region#References_&_Publications|Coutry or Region]].
Comments
We welcome users' contributions to the Wiki. Please click on Comments to view other users' comments, add your own personal experiences or recommend any changes to this page following your visit.
Verified by
Date of member's last visit to North Sea and this page's details validated:
| This is a usable page of the cruising guide. However, please contribute if you can to help it grow further. Click on Comments to add your personal notes on this page or to discuss its contents. Alternatively, if you feel confident to edit the page, click on the edit tab at the top and enter your changes directly. |
| |
|---|
|
Names: Lighthouse |